Permaculture, a contraction of “permanent agriculture,” was developed in Australia in the 1970s by Bill Mollison and David Holmgren. It’s a design system for sustainable land use and living, grounded in ecological principles and three key ethics: care of the Earth, care of people, and fair share. Permaculture is a global movement dedicated to creating a sustainable future through the application of permaculture design principles. Inspired by nature, it seeks to develop self-sufficient and sustainable farming systems that prioritize natural productivity, resilience, crop diversity, and overall sustainability.
Understanding the Ethos of Permaculture
At the core of permaculture is a deep respect for nature and a strong grasp of ecological principles. The three key ethics—Earth Care, People Care, and Fair Share—guide every aspect of permaculture design and practice.
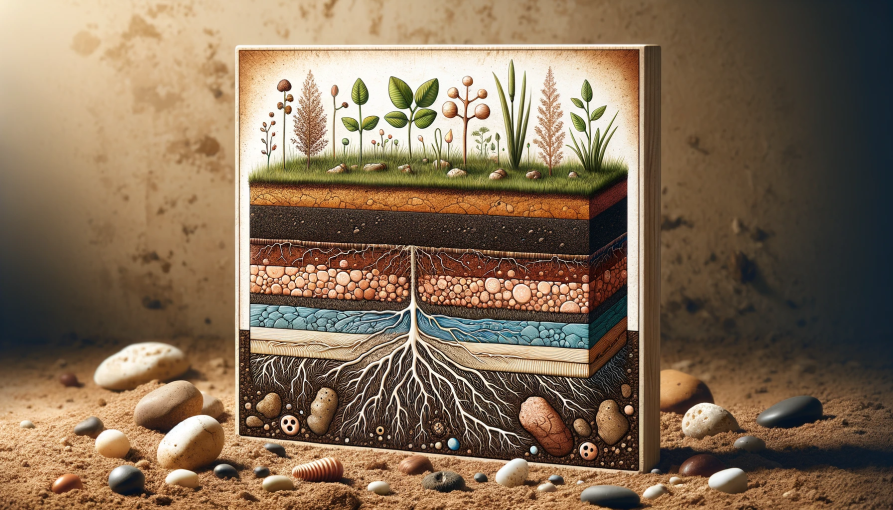
Earth Care values all living beings and ecosystems, focusing on rebuilding natural resources and restoring ecological balance. This involves promoting soil health, conserving water, protecting biodiversity, and reducing environmental impact.
People Care highlights the connection between human well-being and the natural world. It aims to meet human needs while promoting resilience, fairness, and community unity. Providing access to necessities like food, water, and shelter, as well as nurturing social connections and emotional health, are key aspects of people’s care.
Fair Share promotes fairness by distributing resources equally and sharing any surplus. It encourages responsible consumption, sustainable resource management, and collective efforts to address inequalities and create a fairer and more sustainable society.
These principles, influenced by various cultural traditions and indigenous knowledge, are the basis of permaculture. They help individuals and communities develop a balanced and respectful connection with the Earth and with one another.
The Essence of Permaculture Design
Permaculture design is a dynamic and multidisciplinary method for developing sustainable systems that imitate the strength and variety of natural ecosystems. It combines ecological principles, social dynamics, and cutting-edge technologies to create productive, resilient, and self-sufficient landscapes, habitats, and human settlements.
Permaculture design is based on a set of principles that are inspired by observing natural patterns and processes. These principles, developed by Mollison and Holmgren, provide a foundation for creating systems that are efficient, diverse, and harmonious while reducing waste and reliance on external resources.
Some key principles of permaculture design include:
- Observation and Interaction: Take the time to carefully observe and understand the patterns and dynamics of natural systems before taking action. This will help make informed decisions and create responsive designs.
- Catch and Store Energy: Utilize renewable energy sources like sunlight, wind, and water, and store them for future use. This can be done through methods like collecting rainwater, harnessing solar power, and implementing passive heating and cooling techniques.
- Use and Value Renewable Resources and Services: Give priority to using renewable resources and ecological services instead of finite or non-renewable alternatives. This involves utilizing natural processes like nutrient cycling, pollination, and soil regeneration.
- Apply Self-Regulation and Accept Feedback: Design systems that can regulate themselves and adapt to feedback from the environment and stakeholders. This includes promoting resilience, diversity, and redundancy within the systems to withstand disturbances and shocks.
- Produce No Waste: Minimize waste by designing systems that use all outputs as inputs for other components. Permaculture focuses on creating zero-waste systems that are efficient and productive.
- Integrate Rather Than Segregate: Create interconnected systems where each element serves multiple functions to enhance resilience and productivity. This fosters symbiotic relationships between different components.
- Use Small and Slow Solutions: Opt for small-scale, decentralized interventions over large-scale, centralized solutions for greater adaptability and resilience in uncertain conditions.
- Diversity: Enhance resilience and ecosystem health by promoting biodiversity and genetic diversity within systems. Incorporating a wide range of species and functional groups helps systems withstand pests, diseases, and environmental changes.
By applying these principles in conjunction with the ethics of Earth Care, People Care, and Fair Share, permaculture designers can create thriving ecosystems and communities that benefit both people and the planet.
Applications of Permaculture
Permaculture principles and techniques are used in various areas, such as agriculture, agroforestry, urban planning, and community development. Some notable examples of permaculture practices include:
- Regenerative Agriculture: Permaculture takes a comprehensive approach to farming that focuses on the health of the soil, biodiversity, and the resilience of ecosystems. Methods like agroforestry, polyculture, composting, and no-till farming are commonly used to increase productivity while minimizing harm to the environment.
- Water Management: Permaculture offers innovative solutions for sustainable water management, such as collecting rainwater, creating swales and ponds, and using water-efficient irrigation systems. By effectively capturing, storing, and utilizing rainwater, permaculturists can combat droughts, prevent erosion, and replenish underground water sources.
- Ecological Building Design: Permaculture principles are applied in the design and construction of eco-friendly buildings that reduce energy consumption, utilize natural materials, and promote healthy indoor air quality. Techniques like passive solar design, natural ventilation, and green roofs are integrated to create comfortable and energy-efficient living spaces.
- Community Resilience: Permaculture promotes community resilience by encouraging local self-sufficiency, social unity, and collaborative decision-making. Initiatives like community gardens, cooperative housing, tool-sharing networks, and skill-building workshops empower individuals and communities to meet their needs sustainably.
- Habitat Restoration: Permaculture methods help restore damaged ecosystems like farmland, deforested areas, and urban brownfields. By bringing back native plants, improving soil quality, and establishing wildlife corridors, permaculture experts aid in conserving biodiversity and rejuvenating ecosystems.
- Waste Management: Permaculture focuses on reducing, reusing, recycling, and composting to manage both organic and non-organic waste. Methods like vermicomposting, biochar production, and upcycling are used to reduce landfill waste and produce beneficial resources for soil health and plant development.
These are just a few examples of how permaculture principles can be applied to create sustainable, resilient, and regenerative systems across various scales and contexts.
The Environmental Impact of Permaculture
Permaculture holds immense potential to mitigate environmental degradation, restore ecosystems, and build resilience in the face of climate change. By promoting biodiversity, enhancing soil health, conserving water resources, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, permaculture practices contribute to a more sustainable and ecologically balanced world.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Permaculture designs prioritize the integration of various plant and animal species, creating habitats that support a wide range of native plants and animals. By imitating natural ecosystems, permaculture systems help protect biodiversity and endangered species.
- Soil Revitalization: Permaculture techniques like composting, mulching and cover cropping improve soil health and fertility, increasing its ability to store carbon, retain water, and support plant growth. Healthy soils are crucial for agriculture, carbon storage, and ecosystem resilience.
- Water Conservation: Permaculture emphasizes water conservation and efficient use through methods like rainwater harvesting, contour bunding, and greywater recycling. By collecting and storing rainwater, permaculture systems reduce the need for irrigation, alleviate water scarcity, and mitigate the impacts of droughts and floods.
- Carbon Storage: Permaculture practices contribute to carbon storage by enhancing vegetation cover, promoting agroforestry, and increasing organic matter in soils. By storing carbon in plants and soil, permaculture systems help combat climate change and improve climate resilience.
- Erosion Prevention: Permaculture techniques such as contour ploughing, terracing, and windbreaks help prevent soil erosion and land degradation. By stabilizing slopes, improving ground cover, and reducing runoff, permaculture systems protect soil health and maintain the integrity of ecosystems.
- Pollution Reduction: Permaculture promotes organic farming practices, non-toxic pest control methods, and closed-loop nutrient cycles, reducing the use of synthetic inputs and minimizing pollution of air, water, and soil. By adopting regenerative agricultural practices, permaculture systems mitigate environmental pollution and promote the health of ecosystems.
To sum up, permaculture provides a comprehensive and interconnected approach to addressing environmental degradation, food insecurity, social inequity, and climate change. By following the principles of Earth Care, People Care, and Fair Share, permaculture enables individuals and communities to establish regenerative systems that support the land, livelihoods, and thriving ecosystems for future generations.
In conclusion, permaculture goes beyond mere techniques or practices; it encompasses a mindset and lifestyle that harmonizes with nature. By embracing Earth Care, People Care, and Fair Share, we can utilize the transformative potential of permaculture to build a sustainable, fair, and resilient world for everyone.